Our promise to you:
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support.
 24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
 CONTACT US TO ORDER
CONTACT US TO ORDER
Transfected Stable Cell Lines
Reliable | High-Performance | Wide Rage
Precision reporter, kinase, immune receptor, biosimilar, Cas9, and knockout stable cell lines for diverse applications.
Premade Virus Particles
Ready-to-Use | High Titer | Versatile Applications
Premade AAV, adenovirus, lentivirus particles, safe, stable, in stock.
Virus-Like Particles (VLPs)
Stable | Scalable | Customizable
Advanced VLPs for vaccine development (Chikungunya, Dengue, SARS-CoV-2), gene therapy (AAV1 & AAV9), and drug screening (SSTR2, CCR5).
Oligonucleotide Products
Precise | High Yield | Tailored Solutions
Accelerate your research with cost-effective LncRNA qPCR Array Technology.
RNA Interference Products
Targeted | Potent | High Specificity
Human Druggable Genome siRNA Library enables efficient drug target screening.
Recombinant Drug Target Proteins
Authentic | Versatile | Accelerated
Providing functional, high-purity recombinant proteins—including membrane proteins and nanodiscs—to overcome bottlenecks in drug screening and target validation.
Clones
Validated | Reliable | Comprehensive Collection
Ready-to-use clones for streamlined research and development.
Kits
Complete | Convenient | High Sensitivity
Chromogenic LAL Endotoxin Assay Kit ensures precise, FDA-compliant endotoxin quantification for biosafety testing.
Enzymes
Purified | Stable | Efficient
Powerful Tn5 Transposase for DNA insertion and random library construction.
Aptamers
Highly Specific | Robust | Versatile
Aptamers for key proteins like ACVR1A, Akt, EGFR, and VEGFR.
Adjuvants
Enhancing | Synergistic | Effective
Enhance immune responses with high-purity, potent CpG ODNs.
Laboratory Equipment
Innovative | Reliable | High-Precision
Effortlessly streamline DNA extraction with CB™ Magnetic-Nanoparticle Systems.
Stable Cell Line Generation
Reliable | Scalable | Customizable
Fast proposals, regular updates, and detailed reports; strict quality control, and contamination-free cells; knockout results in 4-6 weeks.
Target-based Drug Discovery Service
Innovative | Comprehensive | Efficient
Target identification, validation, and screening for drug discovery and therapeutic development.
Custom Viral Service
Versatile | High-Yield | Safe
Unbeatable pricing, fully customizable viral packaging services (covering 30,000+ human genes, 200+ mammals, 50+ protein tags).
Custom Antibody Service
Precise | Flexible | Efficient
End-to-end antibody development support, from target to validation, enabling clients to rapidly obtain application-ready antibodies.
Antibody-Drug Conjugation Service
Integrated | Controlled | Translational
Comprehensive solutions covering design, development, and validation to ensure conjugated drugs with consistent quality and clinical potential.
Protein Degrader Service
Efficient | High-Precision | Advanced Therapeutics
Harness the power of protein degraders for precise protein degradation, expanding druggable targets and enhancing therapeutic effectiveness for cutting-edge drug discovery.
Nucleotides Service
Accurate | Flexible | High-Quality
Custom synthesis of oligonucleotides, primers, and probes for gene editing, PCR, and RNA studies.
Custom RNA Service
Custom RNA ServicePrecise | Flexible | GMP-ReadyCustom
RNA design, synthesis, and manufacturing—covering mRNA, saRNA, circRNA, and RNAi. Fast turnaround, rigorous QC, and seamless transition from research to GMP production.
Custom Libraries Construction Service
Comprehensive | High-throughput | Accurate
Custom cDNA, genomic, and mutagenesis libraries for drug discovery, screening, and functional genomics.
Gene Editing Services
Precise | Efficient | Targeted
Gene editing solutions for gene editing, knockouts, knock-ins, and customized genetic modifications. Integrated multi-platform solutions for one-stop CRISPR sgRNA library synthesis and gene screening services
Microbe Genome Editing Service
Precise | Scalable | Customizable
Enhance microbial productivity with advanced genome editing using Rec-mediated recombination and CRISPR/Cas9 technologies.
Biosafety Testing Service
Reliable | Comprehensive | Regulated
Complete biosafety testing solutions for gene therapy, viral vectors, and biologics development.
Plant Genetic Modification Service
Advanced | Sustainable | Tailored
Genetic modification for crop improvement, biotechnology, and plant-based research solutions.
Plant-based Protein Production Service
Efficient | Scalable | Customizable
Plant-based protein expression systems for biopharmaceuticals, enzyme production, and research.
Aptamers Service
Innovative | Fast | Cost-Effective
Revolutionizing drug delivery and diagnostic development with next-generation high-throughput aptamer selection and synthesis technologies.
CGT Biosafety Testing
Comprehensive | Accurate | Regulatory-compliant
Internationally certified evaluation system for biologics, gene therapies, nucleic acid drugs, and vaccines.
Pandemic Detection Solutions
Rapid | Precise | Scalable
Balancing accuracy, accessibility, affordability, and rapid detection to safeguard public health and strengthen global response to infectious diseases.
cGMP Cell Line Development
Reliable | Scalable | Industry-leading
Stable expression over 15 generations with rapid cell line development in just 3 months.
Supports adherent and suspension cell lines, offering MCB, WCB, and PCB establishment.
GMP mRNA Production
Efficient | Scalable | Precise
Scalable mRNA production from milligrams to grams, with personalized process design for sequence optimization, cap selection, and nucleotide modifications, all in one service.
GMP Plasmid Production
High Quality | Scalable | Regulatory-compliant
Our plasmid production services span Non-GMP, GMP-Like, and GMP-Grade levels, with specialized options for linearized plasmids.
GMP Viral Vector Manufacturing
Scalable | High Yield | Quality-driven
Advanced platforms for AAV, adenovirus, lentivirus, and retrovirus production, with strict adherence to GMP guidelines and robust quality control.
AI-Driven Gene Editing and Therapy
Innovative | Precision | Transformative
AI-powered one-click design for customized CRISPR gene editing strategy development.
AI-Antibody Engineering Fusion
Next-Generation | Targeted | Efficient
AI and ML algorithms accelerate antibody screening and predict new structures, unlocking unprecedented possibilities in antibody engineering.
AI-Driven Enzyme Engineering
Smart | Efficient | Tailored
High-throughput enzyme activity testing with proprietary datasets and deep learning models for standardized and precise enzyme engineering design.
AI-Enhanced Small Molecule Screening
Predictive | Efficient | Insightful
Leverage AI to uncover hidden high-potential small molecules, prioritize leads intelligently, and reduce costly trial-and-error in early drug discovery.
AI-Driven Protein Degrader Drug Development
Innovative | Targeted | Accelerated
Use AI-guided design to optimize protein degraders, addressing design complexity and enhancing efficacy while shortening development timelines.

Cat.No. : CSC-RO0032 Host Cell: BXPC-3
Size: >1x10^6 cells/vial Validation: T7 Endonuclease I assay
| Cat. No. | CSC-RO0032 |
| Description | BXPC-3-Cas9 cell line is engineered to stably overexpress Cas9 nuclease. The Cas9 nuclease in BXPC-3-Cas9 cell line has been functionally validated using T7 Endonuclease I assay. In combination with separately transfected sgRNAs, BXPC-3-Cas9 cell line can be used to efficiently generate targeted genomic modifications including gene knockout, gene knockin, gene mutagenesis, gene tagging etc. It is also an ideal cell line model for sgRNA screening and validation, either individually or in pools. |
| Introduction | Clustered regularly interspaced palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/Cas9 is a gene-editing technology that contains two essential components: a guide RNA (gRNA) to match a target gene, and the Cas9 (CRISPR-associated protein 9) endonuclease which causes a double-stranded DNA break, allowing modifications to the genome via nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) or homology-directed repair (HDR). |
| Target Gene | Cas9 |
| Host Cell | BXPC-3 |
| Host Cell Species | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| Product Type | Cas9 overexpression stable cell line |
| Applications | 1) CRISPR genome editing, such as gene knockout (KO), gene knockin (KI), gene mutagenesis, gene tagging etc. 2) High-throughput sgRNA screening and validation |
| Quality Control | 1) T7E1 assay 2) Mycoplasma detection |
| Size Form | One vial of frozen cells, typically >1x10^6 cells/vial |
| Shipping | Dry ice |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen |
| Mycoplasma | Negative |
| Format | One frozen vial containing millions of cells |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen |
| Safety Considerations |
The following safety precautions should be observed. 1. Use pipette aids to prevent ingestion and keep aerosols down to a minimum. 2. No eating, drinking or smoking while handling the stable line. 3. Wash hands after handling the stable line and before leaving the lab. 4. Decontaminate work surface with disinfectant or 70% ethanol before and after working with stable cells. 5. All waste should be considered hazardous. 6. Dispose of all liquid waste after each experiment and treat with bleach. |
| Ship | Dry ice |
TGF-β signaling is essential in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) development, altered in all PDAC cases as one of four major pathways. Researchers demonstrate the crucial role of SMAD2/3 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) progression, particularly in SMAD4-null contexts. By investigating TGF-β signaling in PDAC cells lacking SMAD4, they reveal SMAD2/3's oncogenic effects, influencing collective migration through FAK and Rho/Rac signaling pathways. RNA-sequencing analyses unveil a TGF-β gene signature linked to aggressive behavior, facilitated by SMAD2/3 activation. Additionally, clinical data suggests that SMAD4-negative tumors with elevated phospho-SMAD2 levels exhibit increased aggressiveness and poorer prognosis. These findings underscore the complex interplay between TGF-β signaling components in PDAC, highlighting SMAD2/3 as potential therapeutic targets.
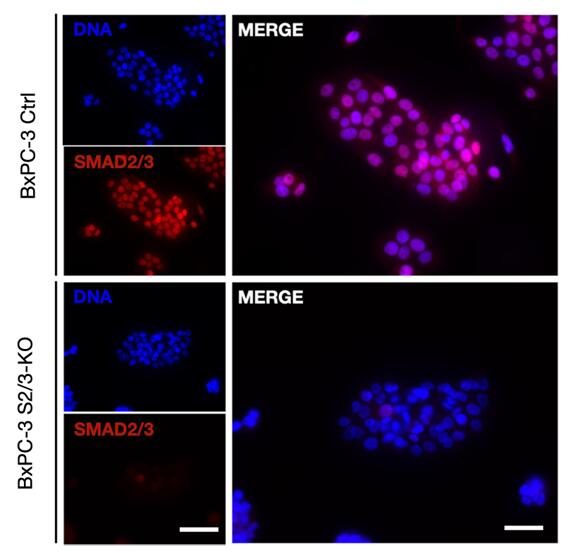 Figure 1. A double SMAD2/SMAD3 knockout BxPC-3 (SMAD4-negative) pancreatic cancer cell line was generated. SMAD protein expression and localization in response to TGF-β treatment were assessed. Altered SMAD2/3 levels and distribution were observed in knockout cells compared to controls, providing insights into TGF-β signaling in pancreatic cancer progression. (Bertrand-Chapel A, et al., 2022)
Figure 1. A double SMAD2/SMAD3 knockout BxPC-3 (SMAD4-negative) pancreatic cancer cell line was generated. SMAD protein expression and localization in response to TGF-β treatment were assessed. Altered SMAD2/3 levels and distribution were observed in knockout cells compared to controls, providing insights into TGF-β signaling in pancreatic cancer progression. (Bertrand-Chapel A, et al., 2022)
Utilizing Creative Biogene's Cas9 Stable Cell Line-BXPC-3 streamlines the process of SMAD2/SMAD3 gene knockout experiments. This stable cell line is directly amenable to CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology, facilitating the rapid generation of SMAD2/SMAD3 knockout cell lines, thereby saving time and resources. Such cell lines can be instrumental in investigating the TGF-β signaling pathway and its implications in pancreatic cancer progression, enhancing the convenience and efficiency of related disease research endeavors.
A: THP-1 cells were likely selected for their monocytic lineage and expression of CD19, making them suitable for evaluating the functionality of the Anti-hCD19-CAR(3G) construct in targeting CD19-positive cells.
A: Stability and expression were likely assessed through flow cytometry, immunoblotting, or functional assays measuring CAR-mediated cytotoxicity or cytokine release, with appropriate selection pressure applied.
A: Characterization may involve analysis of CAR expression levels, binding affinity to CD19, activation-induced signaling pathways, and functional implications in antigen-specific killing of CD19-positive cells.
A: Quality control likely included confirmation of CAR expression and functionality, assessment of off-target effects, and validation of phenotypic changes associated with CAR activation.
A: Comparative analysis with primary T cells or in vivo models helps validate the efficacy and safety of Anti-hCD19-CAR(3G) therapy, guiding its development as a promising treatment for B cell malignancies such as leukemia and lymphoma.
If your question is not addressed through these resources, you can fill out the online form below and we will answer your question as soon as possible.
Remarkable reliability! The Cas9 Stable Cell Line in BXPC-3 cells has been indispensable in our genome editing studies. Its stable expression of Cas9 has facilitated precise and efficient gene modifications, enabling us to dissect the functional significance of specific genetic alterations in cancer.
United States
12/22/2023
Trustworthy and effective! The stable expression of Cas9 in BXPC-3 cells has allowed us to perform targeted genome editing with high accuracy and fidelity. Its consistent Cas9 expression has ensured reliable and reproducible results, enhancing the reliability of our experiments.
United States
07/09/2022
Streamlining our research! With the Cas9 Stable Cell Line, we've been able to investigate the role of specific genes in cancer development and progression with confidence. Its stable expression of Cas9 has streamlined experimental workflows and accelerated the pace of our research.
Germany
01/19/2021
Impressive performance! The Cas9 Stable Cell Line has consistently exhibited efficient Cas9-mediated genome editing, exceeding our expectations. Its stable expression has been instrumental in unraveling the genetic determinants of cancer phenotypes and identifying potential therapeutic targets.
Canada
08/31/2022
A valuable tool in cancer genomics! The Cas9 Stable Cell Line has transformed our understanding of cancer biology. Its stable expression of Cas9 has provided a versatile platform for exploring gene function and dissecting molecular mechanisms underlying tumorigenesis.
United States
04/06/2020
Write a review of your use of Biogene products and services in your research. Your review can help your fellow researchers make informed purchasing decisions.

Our promise to you:
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support.
 24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
 CONTACT US TO ORDER
CONTACT US TO ORDER

Copyright © Creative Biogene. All rights reserved.