Our promise to you:
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support.
 24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
 CONTACT US TO ORDER
CONTACT US TO ORDER
Cat.No. : CSC-RT0708
Host Cell: HeLa Target Gene: AHR
Size: 1x10^6 cells/vial, 1mL Validation: Sequencing
| Cat. No. | CSC-RT0708 |
| Description | A stable cell line with a homozygous knockout of human AHR using CRISPR/Cas9. |
| Target Gene | AHR |
| Host Cell | HeLa |
| Host Cell Species | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| Shipping | 10^6 cells/tube |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen |
| Revival | Rapidly thaw cells in a 37°C water bath. Transfer contents into a tube containing pre-warmed media. Centrifuge cells and seed into a 25 cm2 flask containing pre-warmed media. |
| Media Type | Cells were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. |
| Growth Properties | Cells are cultured as a monolayer at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. Split at 80-90% confluence, approximately 1:4-1:6. |
| Freeze Medium | Complete medium supplemented with 10% (v/v) DMSO |
| Mycoplasma | Negative |
| Format | One frozen vial containing millions of cells |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen |
| Safety Considerations |
The following safety precautions should be observed. 1. Use pipette aids to prevent ingestion and keep aerosols down to a minimum. 2. No eating, drinking or smoking while handling the stable line. 3. Wash hands after handling the stable line and before leaving the lab. 4. Decontaminate work surface with disinfectant or 70% ethanol before and after working with stable cells. 5. All waste should be considered hazardous. 6. Dispose of all liquid waste after each experiment and treat with bleach. |
| Ship | Dry ice |
Sphingolipid biosynthesis produces lipids required for membranes and signaling, which is essential for many developmental and physiological processes. In some cases, large amounts of specific sphingolipids must be synthesized to achieve specialized physiological functions, such as during axon myelination. How sphingolipid synthesis is regulated to meet these physiological needs is unclear. Here, researchers screened and identified several genes required for Gb3 synthesis in the sphingolipid biosynthesis pathway, and also identified the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR), a ligand-activated transcription factor widely involved in development and physiology, as required for Gb3 biosynthesis. Cell surface Gb3 levels were significantly reduced in AHR knockout HeLa cells, and both AHR knockout HeLa cells and tissues from Ahr knockout mice displayed decreased sphingolipid content as well as significantly reduced expression of several key genes in the sphingolipid biosynthetic pathway. Sciatic nerves from Ahr knockout mice showed reduced ceramide content and reduced myelin thickness. These results suggest that AHR upregulates sphingolipid levels and is important for complete axonal myelination, which requires elevated membrane sphingolipid levels.
To directly determine whether AHR regulates SL levels, an AHR knockout (AHR KO) HeLa cell line was generated by Cas9-mediated disruption of the AHR gene (Figure 1A). Cell surface expression of Gb3 was significantly reduced in AHR KO HeLa cells compared with control cells (Figure 1B). Ceramide levels of some individual species and total ceramide were significantly reduced in AHR KO cells compared with control HeLa cells (Figure 1C). In the absence of AHR, mRNA expression of SL biosynthesis pathway genes SPTSSA, KDSR, UGCG, B4GALT5, and A4GALT was significantly reduced, while CERS2 expression was enhanced (Figure 1D). These results indicate that AHR is required for the normal expression of several key genes in the Gb3 biosynthesis pathway and that SL levels (ceramide and Gb3) are both reduced in the absence of AHR.
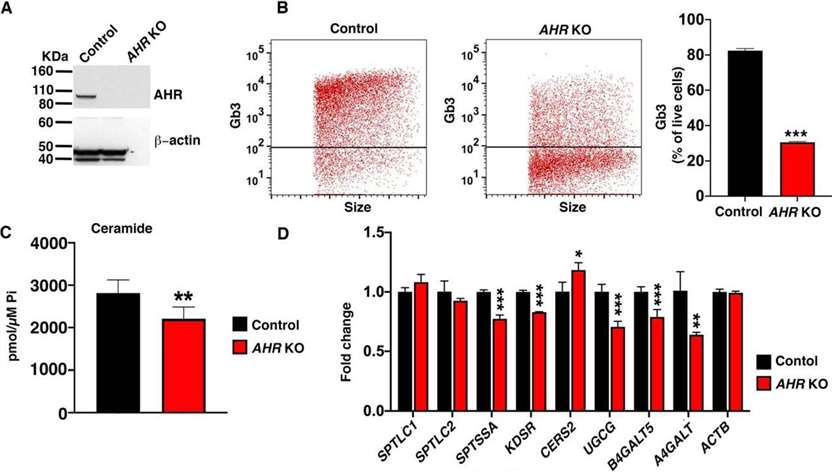 Figure 1. AHR is a positive regulator of SL levels in HeLa cells. (Majumder, Saurav, et al. 2020)
Figure 1. AHR is a positive regulator of SL levels in HeLa cells. (Majumder, Saurav, et al. 2020)
A: DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum.
It is not required to add the selection antibiotics when culturing the KO cells.
A: The knockout cell product is validated by PCR amplification and Sanger Sequencing to confirm the mutation at the genomic level. Please find the detailed mutation info in the datasheet.
A: Single clonal cell.
A: No. This knockout cell product is generated using the CRISPR/Cas9 system to induce small insertions or deletions (indels) resulting in frameshift mutations. Although these frameshift mutations typically disrupt the coding gene, there is a possibility that the non-functional transcript may still be transcribed. Consequently, this could potentially yield misleading results when analyzed by RT-qPCR.
A: The cell line should be stored in liquid nitrogen for long-term preservation.
A: For most cases, we often keep at least 2 clones with different frameshift mutations. Please feel free to contact us to check if there are additional available clones.
If your question is not addressed through these resources, you can fill out the online form below and we will answer your question as soon as possible.
This knockout cell line has proved versatile in various experimental setups, ranging from drug screening to basic research on AHR signaling pathways.
The Human AHR Knockout Cell Line-HeLa has provided us with distinct phenotypic differences that are easy to quantify, making our data robust and publication-ready.
Write a review of your use of Biogene products and services in your research. Your review can help your fellow researchers make informed purchasing decisions.
Our promise to you:
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support.
 24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
24x7 CUSTOMER SERVICE
 CONTACT US TO ORDER
CONTACT US TO ORDER