Transfected Stable Cell Lines
Reliable | High-Performance | Wide Rage
Precision reporter, kinase, immune receptor, biosimilar, Cas9, and knockout stable cell lines for diverse applications.
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Price |
|---|---|---|
| CSC-DC007597 | Panoply™ Human IL33 Knockdown Stable Cell Line | Inquiry |
| CSC-SC007597 | Panoply™ Human IL33 Over-expressing Stable Cell Line | Inquiry |
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Price |
|---|---|---|
| CSC-DC007597 | Panoply™ Human IL33 Knockdown Stable Cell Line | Inquiry |
| CSC-SC007597 | Panoply™ Human IL33 Over-expressing Stable Cell Line | Inquiry |
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Price |
|---|---|---|
| CSC-DC007597 | Panoply™ Human IL33 Knockdown Stable Cell Line | Inquiry |
| CSC-SC007597 | Panoply™ Human IL33 Over-expressing Stable Cell Line | Inquiry |
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Price |
|---|---|---|
| CSC-DC007597 | Panoply™ Human IL33 Knockdown Stable Cell Line | Inquiry |
| CSC-SC007597 | Panoply™ Human IL33 Over-expressing Stable Cell Line | Inquiry |
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Price |
|---|---|---|
| CSC-DC007597 | Panoply™ Human IL33 Knockdown Stable Cell Line | Inquiry |
| CSC-SC007597 | Panoply™ Human IL33 Over-expressing Stable Cell Line | Inquiry |
IL33 is a member of the IL-1 family and a ligand for the orphan receptor ST2 (also known as IL-1RL1); it plays a crucial role in innate and adaptive immunity, contributing to tissue homeostasis and responses to environmental stress. IL33 plays an important role in regulating infections and autoimmune diseases.
IL33 is primarily released by endothelial cells, epithelial cells, and fibroblasts during tissue damage and/or mechanical stress. Upon release, IL33 acts as an alarmin and activates various cell types, including Th2 cells, Tregs, basophils, mast cells, eosinophils, macrophages, dendritic cells, innate lymphoid cells (ILC2), NK cells, and NKT cells. These cells respond to IL33/ST2 signaling by producing pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory mediators according to the immune environment in different tissues and diseases.
The interleukin-33 (IL33) gene is located on the short arm of chromosome 9 at 9p24.1 and consists of 270 amino acids. Full-length IL33 contains two highly conserved domains: an N-terminal nuclear domain with nuclear localization and chromatin-binding motifs, and a C-terminal IL-1-like cytokine domain. IL33 contains a conserved β-trefoil conformation and a central hydrophobic core composed of 12 β-sheets. Two ST2 binding sites have been identified in IL33. IL33 signals through its specific primary receptor ST2 and co-receptor IL-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP); in the ternary complex, the juxtaposition of the cytoplasmic Toll/IL-1R (TIR) domains of ST2 and IL-1RAcP leads to activation of intracellular signaling pathways.
IL33 is localized in the nucleus of expressing cells and becomes biologically active when released after cell damage or necrotic cell death. The binding of full-length or mature IL33 to ST2 and IL-1RAcP (an accessory receptor of the IL-1 superfamily) results in the association of MyD88, IRAK1, and IRAK4 kinases with TRAF6, and activates several MAP kinases and NF-κB.
IL33 binding to ST2, which is upregulated on activated CD8+ T cells, CD4+ Th1 cells, and NK cells, leads to enhanced proliferation and increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Cells that mediate type 2 immunity express ST2 and respond to IL33 by proliferating and producing cytokines that support pathogen clearance and restoration of epithelial health. IL-13 produced by ILC2s, CD4+ Th2 cells, Tregs, and basophils is crucial for generating reparative and regulatory macrophages that assist in repair and support local Tregs.
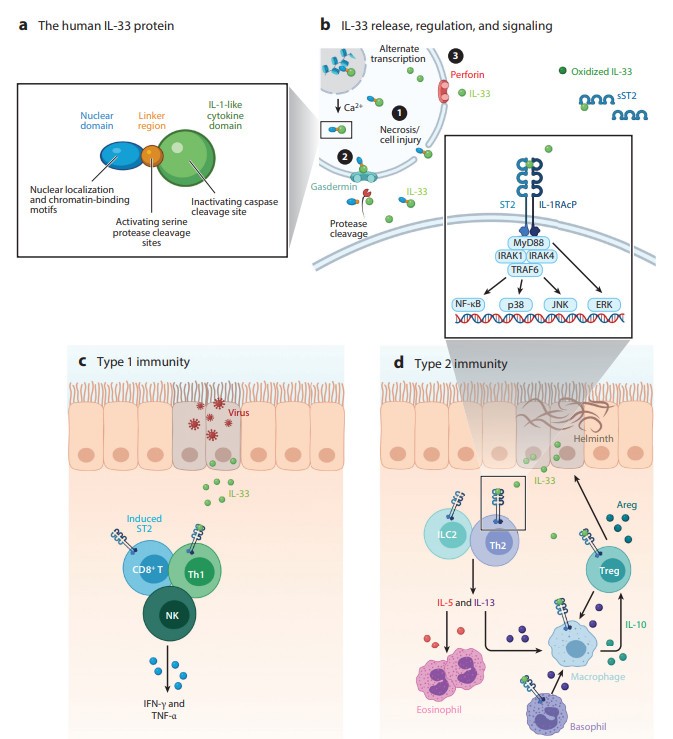 Figure 1. Structure and function of IL-33 in immunity. (Gabryelska A, et al., 2019)
Figure 1. Structure and function of IL-33 in immunity. (Gabryelska A, et al., 2019)
IL33 plays an important role in regulating inflammatory responses and has pro-inflammatory effects in inflammatory diseases such as sepsis and asthma. In sepsis, IL33 exerts pro-inflammatory effects by activating type 2 immune responses and enhancing immune cell function, participating in the regulation of inflammatory processes. It helps regulate the activity of neutrophils and ILC2s, promotes bacterial clearance at infection sites, and may influence the severity and prognosis of sepsis.
IL33 also plays an important role in chronic respiratory diseases, such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). In these diseases, serum levels of IL33 are elevated and correlate with disease severity.
Tozorakimab
Tozorakimab is a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-33 developed by AstraZeneca. It has a dual mechanism of action, effectively inhibiting IL-33-driven ST2-dependent inflammatory responses and preventing IL-33 oxidation and its activity through the RAGE/EGFR signaling pathway, thereby increasing epithelial cell migration and repair.
Published Phase 1 clinical trial results show that Tozorakimab effectively reduces levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-5 and IL-13 in the serum of COPD patients. Currently, Tozorakimab is undergoing multiple international multicenter Phase 3 clinical studies for indications including COPD, asthma, and viral lung infections requiring oxygen therapy.
Itepekimab
Itepekimab is an anti-IL-33 monoclonal antibody developed through collaboration between Sanofi and Regeneron. Published results from a Phase 2a trial (NCT03546907) evaluating its safety and efficacy in moderate to severe COPD patients on triple or dual inhaled maintenance therapy showed that Itepekimab did not demonstrate statistically significant reduction in acute exacerbation rates across all populations. However, subgroup analysis showed it could reduce acute exacerbation rates and improve lung function in former smokers.
Currently, two Phase 3 studies evaluating the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of Itepekimab in former smokers with moderate to severe COPD are ongoing: AERIFY1 (NCT04701983) and AERIFY2 (NCT04751487). Sanofi is very optimistic about Itepekimab, predicting its peak annual sales for COPD indication could exceed 5 billion euros.
Other IL-33 Drugs
REGEND001, Torudokimab, and PF-07264660 have entered Phase 2 clinical trials.
Torudokimab is a fully human, high-affinity antibody targeting IL-33 that Zura Bio licensed from Eli Lilly, currently in Phase 2 clinical trials. Published Phase 1 and 2 clinical trial results show that Torudokimab is well-tolerated and demonstrates efficacy in diseases caused by epithelial inflammation.
Despite positive progress with multiple IL-33 targeted drugs, the future of IL-33 remains uncertain. Several IL-33 target drugs, such as Etokimab and PF-06817024, have not progressed smoothly. Etokimab failed in Phase 2 clinical trials for atopic dermatitis, and PF-06817024 was abandoned by Pfizer.
PF-07264660 is a tri-specific antibody developed by Pfizer targeting IL-4, IL-13, and IL-33, with clinical trials for atopic dermatitis having entered Phase 2.
References
If you don’t find the cell line you want, Creative Biogene can also provide stable cell line generation service with the best prices and fastest turnaround time for you! Contact us for more information or to request a quote.
Inquiry