Autoimmune diseases are the result of the immune system "killing each other", and the core mechanism is the disorder of the immune system's self-recognition function, which leads to inflammatory response and tissue damage. There are more than 100 known autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes, etc.
In the past 30 years, targeting the signaling pathways that regulate immune responses has become a "hot" method for treating autoimmune diseases. The field of autoimmune diseases not only has a fast market growth rate, but also often sees the birth of blockbuster drugs. According to BioSpace statistics, among the top 10 global drug sales in 2024, 4 are autoimmune drugs, with a total sales of US$44 billion, including Sanofi/Regeneron's Dupixent (dupirumab), AbbVie's Skyrizi (risankizumab), Humira (adalimumab), and Johnson & Johnson's Stelara (ustekinumab).
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Price |
|---|---|---|
| CSC-BS0001 | Rituximab Stable Cell Line - CHO-K1 | Inquiry |
| CSC-BS0002 | Trastuzumab Stable Cell Line - CHO-K1 | Inquiry |
| CSC-BS0003 | Cetuximab Stable Cell Line - CHO-K1 | Inquiry |
| CSC-BS0004 | Nivolumab Stable Cell Line - CHO-K1 | Inquiry |
| CSC-BS0005 | Pembrolizumab Stable Cell Line - CHO-K1 | Inquiry |
| CSC-BS0006 | Adalimumab Stable Cell Line - CHO-K1 | Inquiry |
| CSC-BS0007 | Infliximab Stable Cell Line - CHO-K1 | Inquiry |
Recently, Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, a journal that leads the way in drug discovery research, published an article titled "Trends in the drug target landscape for autoimmune diseases", analyzing the development trends of drug targets for autoimmune diseases from 2020 to 2024. The next "king of drugs" may be born from these targets.
The article counted 92 autoimmune disease drug-related targets or target combinations under development in the past five years and found that the number of autoimmune disease drug targets under development increased from 131 in 2020 to 193 in 2024, a "surge" of 47%. Figure 1 shows the dynamic changes in the number of autoimmune disease drug targets under development and on the market from 2020 to 2024.
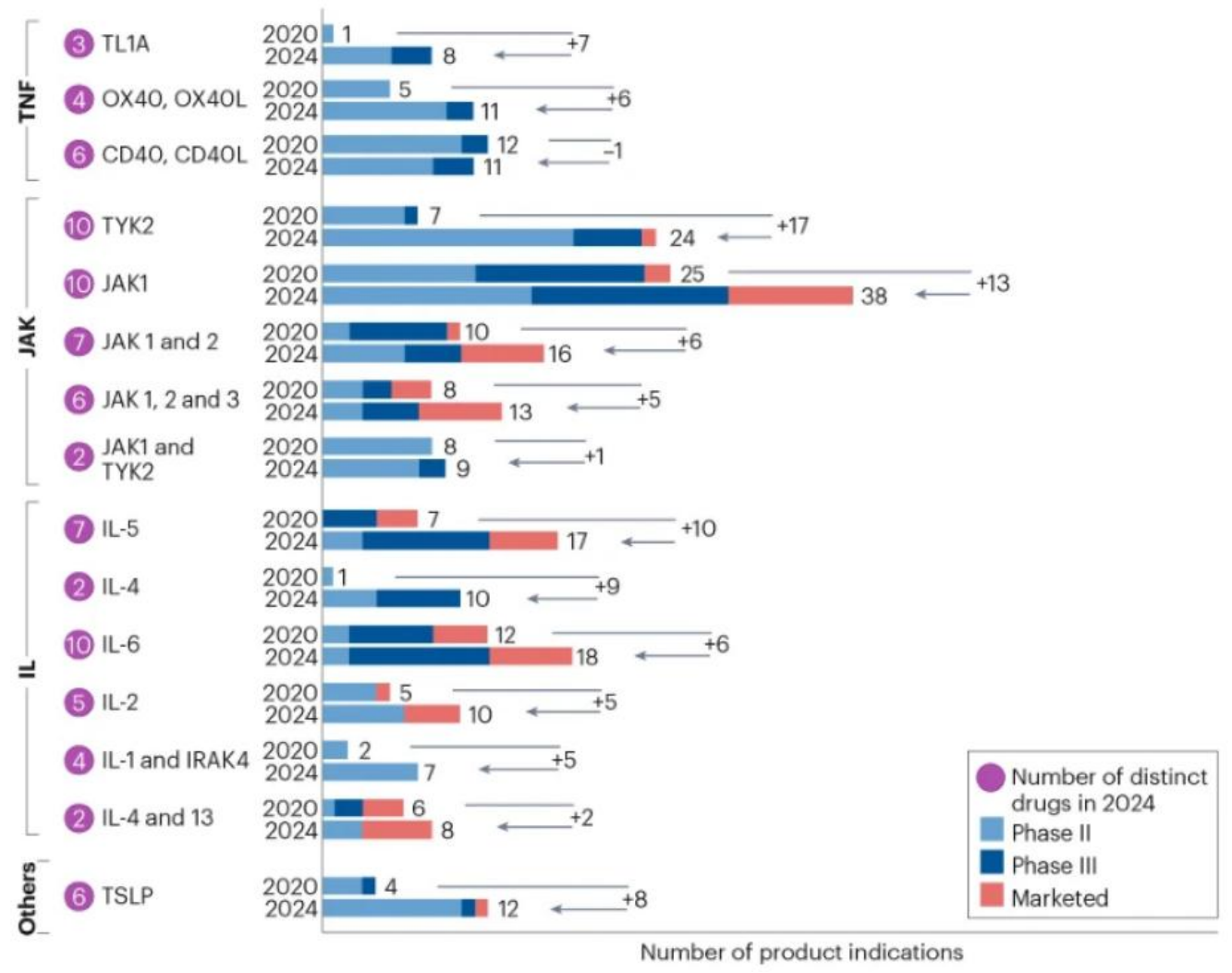
Figure 1. Statistics of popular autoimmune disease drug targets. (Fauconnier A, et al.)
In the past five years, at least four "first-in-class" drugs for autoimmune diseases have been launched, targeting IL-13, IL-31, IL-36 and TYK2 respectively, and the indications are mainly skin autoimmune diseases, such as atopic dermatitis, nodular prurigo, and psoriasis.
The research and development of targets of the TNF superfamily has made significant progress. In 2020, in addition to TNFα, only CD40-CD40L entered clinical phase III. By 2024, drugs targeting OX40, TL1A, RANK, BAFF and other targets have also entered clinical phase III. For example, there are three drugs for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease targeting TL1A that have entered phase III, namely Duvakitug (from Sanofi), RG6631 (from Roche) and Tulisokibart (from Merck).
Innovative research targeting interleukins is driven by a variety of factors, such as higher selectivity (IL-17A/F inhibitors), longer duration of activity (GSK's long-acting IL-15 inhibitors), and the application of new technologies (Eli Lilly's oral drug targeting IL-17). IL-4, IL-18, and IL-33 have the potential to become "first-in-class" targets. The IL-1 receptor-associated kinase IRAK4 has attracted much attention because it is expected to inhibit the entire IL-1 family (IL-1, IL-18, IL-33, IL-36) with one drug. These interleukin factor targets are associated with psoriasis and asthma. The TSLP target has also attracted much attention because it acts on type 2 inflammatory activators IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13.
TYK2 inhibitors are receiving increasing attention. TYK2 acts downstream of the immune response, is associated with the IL-12 and IL-23 signaling pathways, and is involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and Crohn's disease. Compared with JAK inhibitors, TYK2 inhibitors do not affect hematopoietic function. There are currently a variety of combination therapy strategies used to further expand treatment options, such as simultaneously targeting IL-17 and TNF, or using dual kinase inhibitors (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3 and TYK2, SYK, TEC). In 2023, LITFULO (Ritlecitinib) developed by Pfizer was approved by the FDA for the treatment of severe alopecia areata patients over 12 years old. LITFULO is an oral covalent JAK3/TEC dual kinase inhibitor that inhibits the signal transduction of IL-15 and CD8 cytokines, thereby inhibiting the immune system from killing hair follicle cells to achieve the purpose of treating alopecia areata.
Reference
Fauconnier A, et al. Trends in the drug target landscape for autoimmune diseases. Nature reviews. Drug discovery.