Alzheimer's disease (AD) is an age-related neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive memory loss and cognitive dysfunction. It is characterized by amyloid β (Aβ) plaque deposition and neuroinflammation, which plays a central role in the pathogenesis of AD as it exacerbates Aβ and Tau pathology.
Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-activated protein kinase R (PKR) participates in key inflammatory pathways in its activated phosphorylated form (p-PKR). Depletion of PKR has shown potential in rescuing synaptic and learning deficits in Alzheimer's disease mice, making it a potential therapeutic target. However, current small molecule PKR inhibitors often cause side effects such as organ toxicity, which hinders their clinical application.
Circular RNA (circRNA) is a class of single-stranded, covalent RNA molecules with a closed loop structure. In the past decade, studies have found that circRNA is ubiquitously expressed and has specific pathways and rules for generation, processing, degradation, metabolism and function. Compared with linear RNA, circRNA has high stability, special folding and low immunogenicity, which makes it have potential biomedical applications such as transformation into new RNA aptamers and protein translation vectors. It is worth noting that circular RNA (ds-cRNA) with an imperfect RNA double-stranded structure of 16-26bp exhibits a strong PKR inhibitory effect, which suggests that it may solve the problem of PKR overactivation in Alzheimer's disease.
Recently, a research team from the Chinese Academy of Sciences published a research paper entitled "Circular RNA aptamers targeting neuroinflammation ameliorate Alzheimer disease phenotypes in mouse models" in the journal Nature Biotechnology. The study showed that circRNA aptamers delivered by adeno-associated virus (AAV) can safely and effectively inhibit overactivated protein kinase R (PKR), thereby reducing neuroinflammation and β-amyloid protein (Aβ) plaques, achieving neuroprotection for Alzheimer's disease mice and enhancing their spatial learning and memory abilities. These findings suggest that circRNA aptamers have therapeutic potential as PKR inhibitors in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Previously, researchers optimized a new method for RNA self-splicing to form a circle, and achieved large-scale synthesis of low-immunogenicity and special double-stranded structure circRNA aptamers (ds-cRNA). The mechanism of action of ds-cRNA and protein kinase R (PKR) was elucidated at the single-molecule level. The binding of PKR to ds-cRNA presents a long-term, low-dissociation stable binding mode, indicating that ds-cRNA provides a spatial conformation that is more suitable for PKR binding and limits its dissociation.
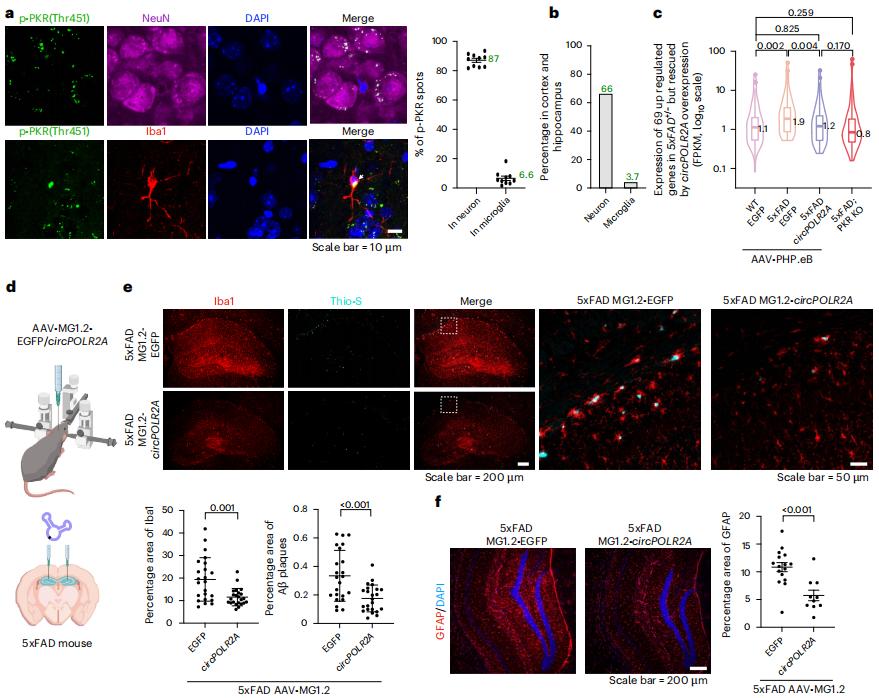
Figure 1. ds-cRNAs rescue AD phenotypes by targeting PKR in neurons and microglia. (Feng X, et al., 2025)
The study further confirmed that in the Alzheimer's disease mouse model, the use of adeno-associated virus AAV-PHP.eB that can break through the blood-brain barrier to deliver circRNA aptamers (ds-cRNA) with a special double-stranded structure to the brain can effectively inhibit over-activated protein kinase R (PKR). With almost no toxic effects, neuroinflammation and β-amyloid protein (Aβ) plaques are reduced, thereby achieving neuroprotection for Alzheimer's disease mice and enhancing their spatial learning and memory abilities. Furthermore, delivery of circRNA aptamers (ds-cRNA) at different stages of Alzheimer's disease progression can alleviate disease phenotypes, and the therapeutic effect lasts for at least 6 months after a single administration.
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Price |
|---|---|---|
| AAV00308Z | AAV PHP.eB-Syn-GFP | Inquiry |
| AAV00306Z | AAV PHP.eB-CAG-Cre | Inquiry |
| AAV00537Z | CMV-mCherry AAV (Serotype PHP.eB) | Inquiry |
| AAV00303Z | scAAV PHP.eB-CMV-GFP | Inquiry |
| AAV00307Z | AAV PHP.eB-CAG-Cre-GFP | Inquiry |
| AAV00538Z | hSyn-NULL AAV (Serotype PHP.eB) | Inquiry |
| AAV00117Z | AAV PHP.eB-Null | Inquiry |
| AAV00302Z | AAV PHP.eB-CMV-GFP | Inquiry |
| AAV00304Z | AAV PHP.eB-CMV-Cre | Inquiry |
| AAV00305Z | AAV PHP.eB-CAG-GFP | Inquiry |
| AAV00309Z | AAV PHP.eB-Syn-Cre | Inquiry |
| AAV00415Z | scAAV PHP.eB-CAG-GFP | Inquiry |
These findings suggest that ds-cRNA aptamers have therapeutic potential as PKR inhibitors in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Overall, this study proposes adeno-associated virus (AAV) delivery of ds-cRNA as an emerging therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer's disease. By targeting overactivated PKR, neuroinflammation and disease progression are inhibited. In addition, considering the long-term therapeutic challenges that may be posed by the immunogenicity of AAV capsids, the development of brain-specific lipid nanoparticles for the delivery of low-immunogenic ds-cRNA can be explored in the future.
Reference
Feng X, et al. Circular RNA aptamers targeting neuroinflammation ameliorate Alzheimer disease phenotypes in mouse models[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2025: 1-10.