• Adenovirus Service • AAV Service • Lentivirus Service • Retrovirus Service


Hyperuricemia (HU) is a metabolic disease caused by high serum uric acid (SUA) levels due to insufficient renal excretion, excessive production, or insufficient intestinal excretion. Various conventional treatments are commonly used to treat HU, such as valproic acid and allopurinol (xanthine oxidase inhibitor). Valproic acid increases urination, thereby enhancing the excretion of urate crystals, while allopurinol relieves symptoms by reducing uric acid production by inhibiting xanthine oxidase. However, increased urination increases the excretion of urate crystals, leading to kidney damage.
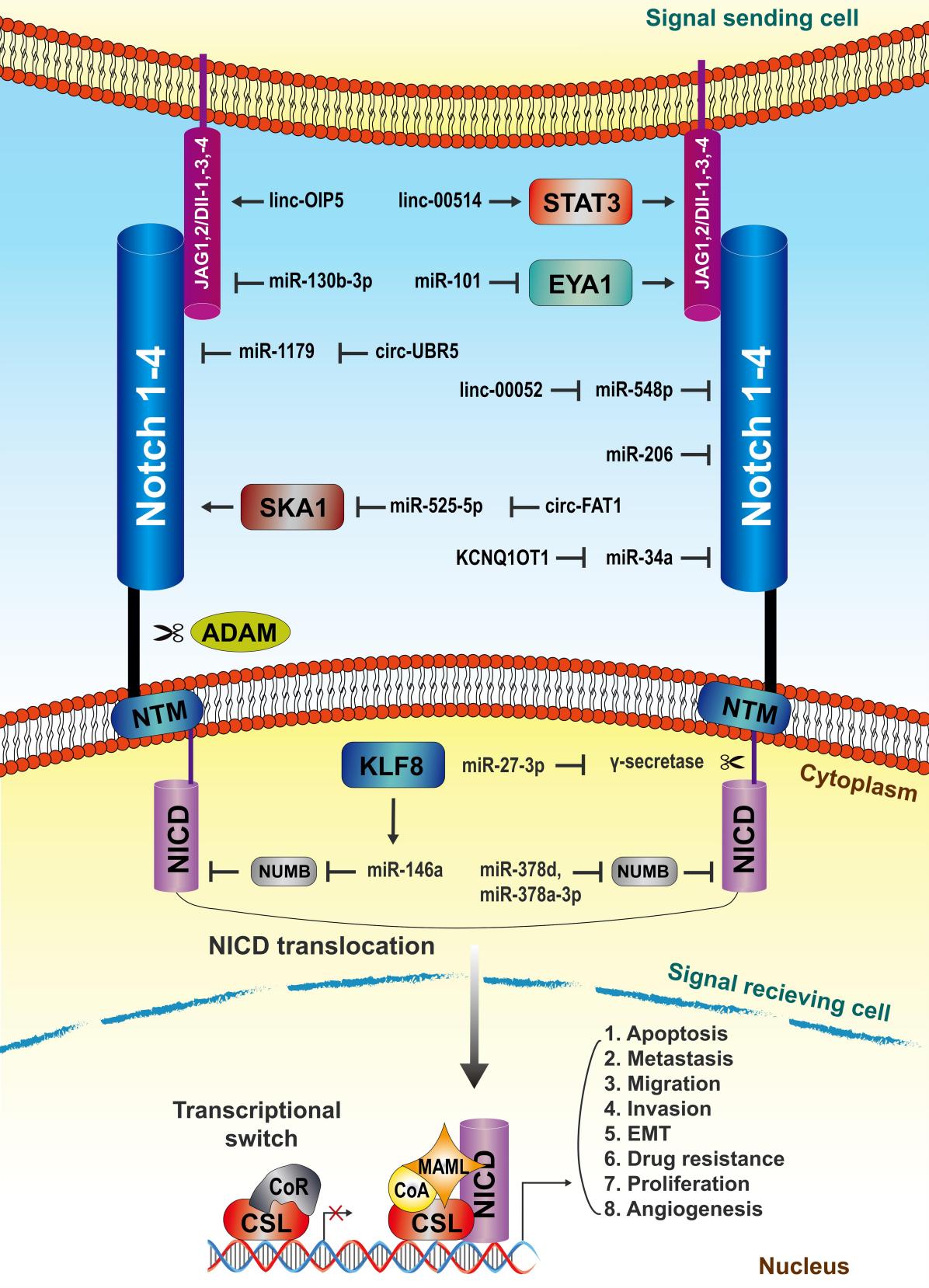
Breast cancer remains one of the most challenging cancers, mainly due to its heterogeneity and metastatic propensity. The Notch signaling pathway is required for multiple cellular processes and is involved in the development and progression of breast cancer. Noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) have now become key regulators of gene expression, which can affect the biology of cancer by interacting with the Notch signaling pathway. Noncoding RNAs include microRNAs, long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs). Recently, in a review report published in the international journal Gene Expression, entitled "Non-coding RNAs Affect Breast Cancer Development Through the Notch Signaling Pathway: An Overview", researchers from Tabriz University outlined the importance of ncRNAs in human breast cancer and their potential as therapeutic targets, paving the way for the development of innovative therapies to significantly impact patient care and prognosis.
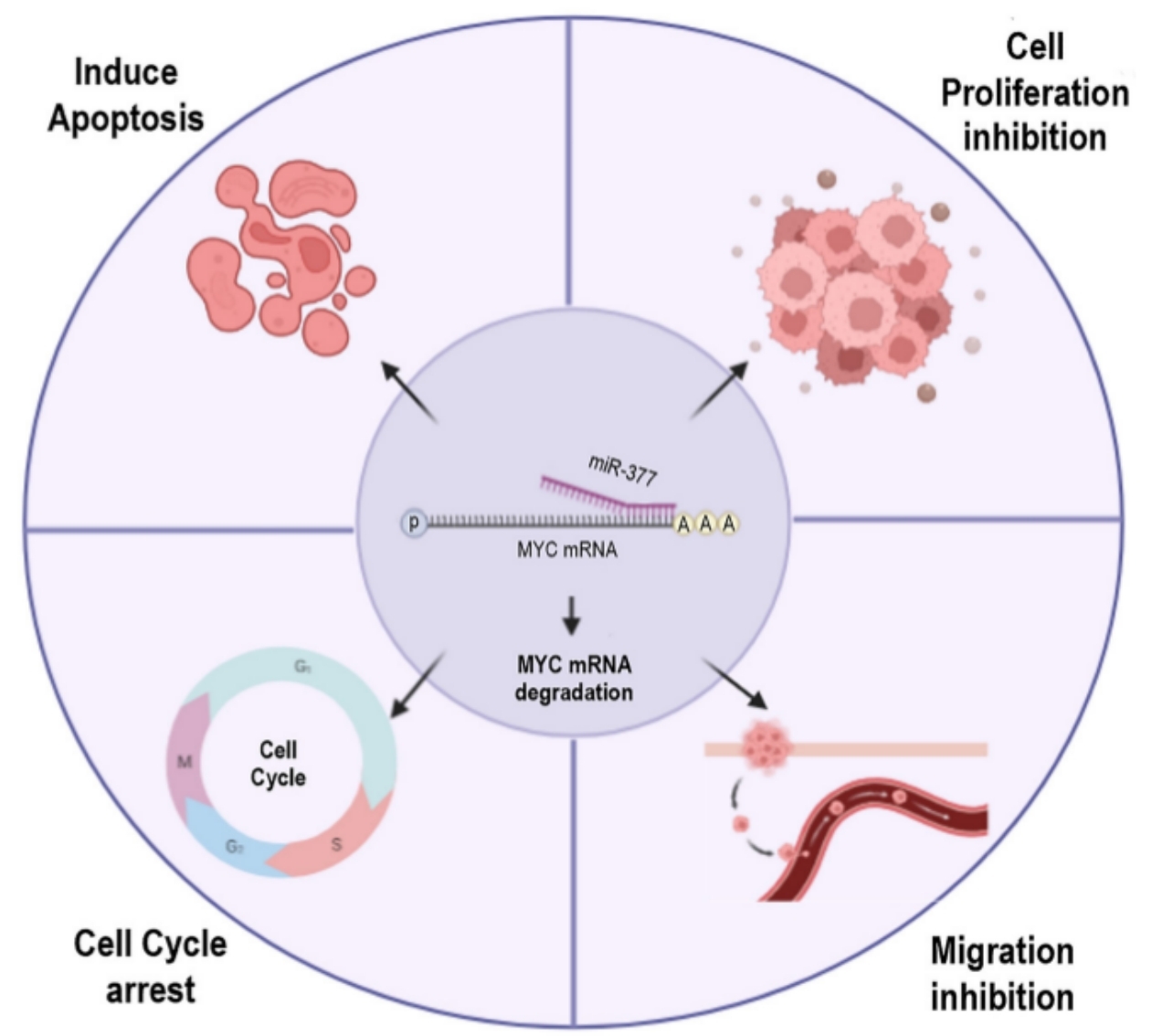
The MYC gene is a regulatory and proto-oncogene that is overexpressed in most prostate cancers (PCa). A large number of research results have shown that abnormal expression of microRNAs is involved in the occurrence and progression of human prostate cancer. Recently, in a research report entitled "Inhibitory effect of miR-377 on the proliferative and invasive behaviors of prostate cancer cells through the modulation of MYC mRNA via its interaction with BCL-2/Bax, PTEN, and CDK4" published in the international journal Genes & Cancer, scientists from the Pasteur Institute of Iran and other institutions revealed the inhibitory effect of miR-377 on prostate cancer cells through research.

In recent years, the potential of RNA vaccines in cancer treatment has attracted widespread attention. With the successful launch of the COVID-19 vaccine, RNA technology has demonstrated its potential for rapid development and customization, bringing new hope to cancer treatment. Recently, Nature's report "How personalized cancer vaccines could keep tumours from coming back" explored the application of RNA vaccines in personalized cancer treatment, especially its prospects in the treatment of melanoma.
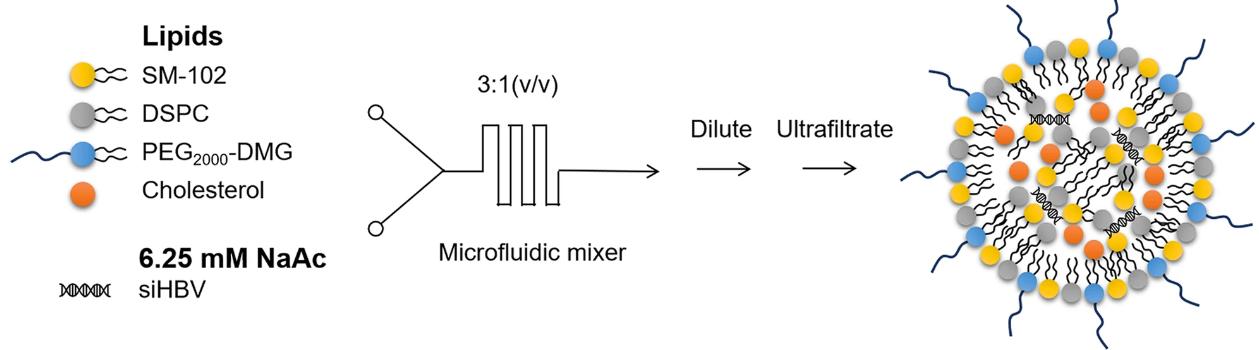
RNA interference (RNAi) technology has shown great potential in the treatment of genetic diseases and viral infections. It is also considered an attractive therapeutic approach to achieve functional cure of hepatitis B by inducing antigen suppression, reducing viremia, and silencing covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA). siRNA-based therapies can also alleviate immune tolerance induced by high viral antigens, providing opportunities for subsequent immune stimulation to gain immune control of the virus.
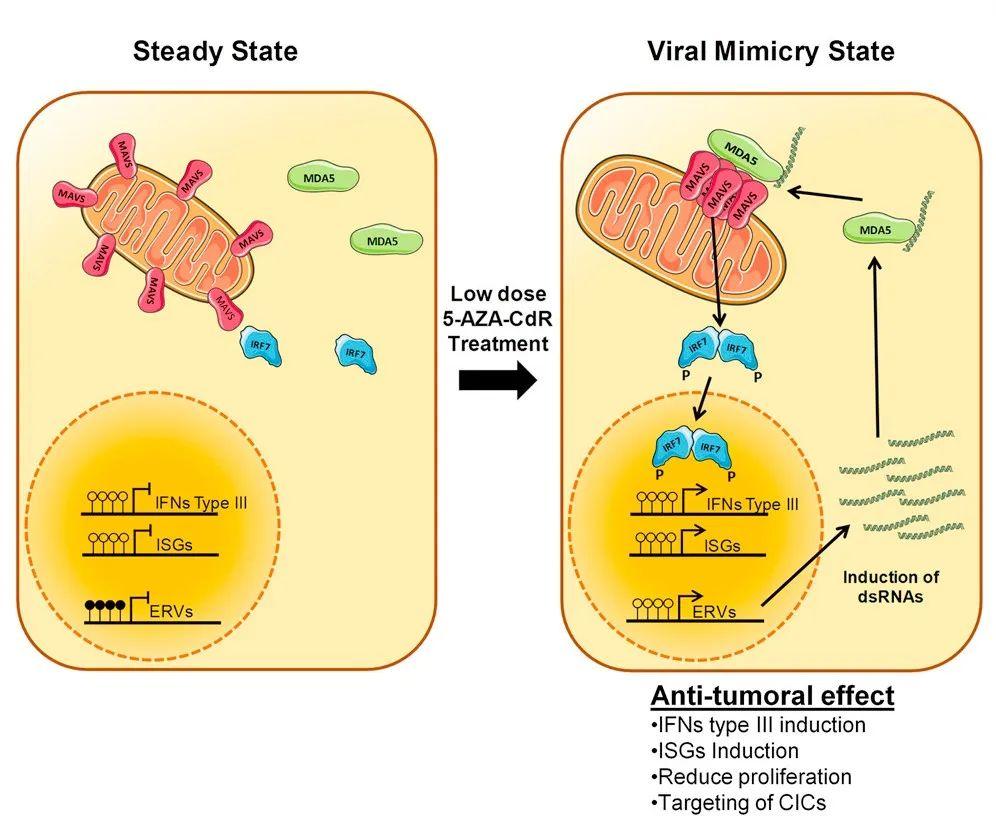
Recently, Cancer Discovery journal published the latest research results led by the research team of Fox Chase Cancer Center in the United States, which proposed a new strategy for transforming the immune microenvironment of "cold" tumors such as small cell lung cancers (SCLCs). With the help of screening based on CRISPR technology, the study found that inhibiting RNA helicase DHX9 can increase endogenous nucleic acids such as double-stranded RNA in cancer cells. Then a state similar to viral infection is created to activate "endogenous immune" mechanisms such as interferon response and successfully transform "cold" tumors.
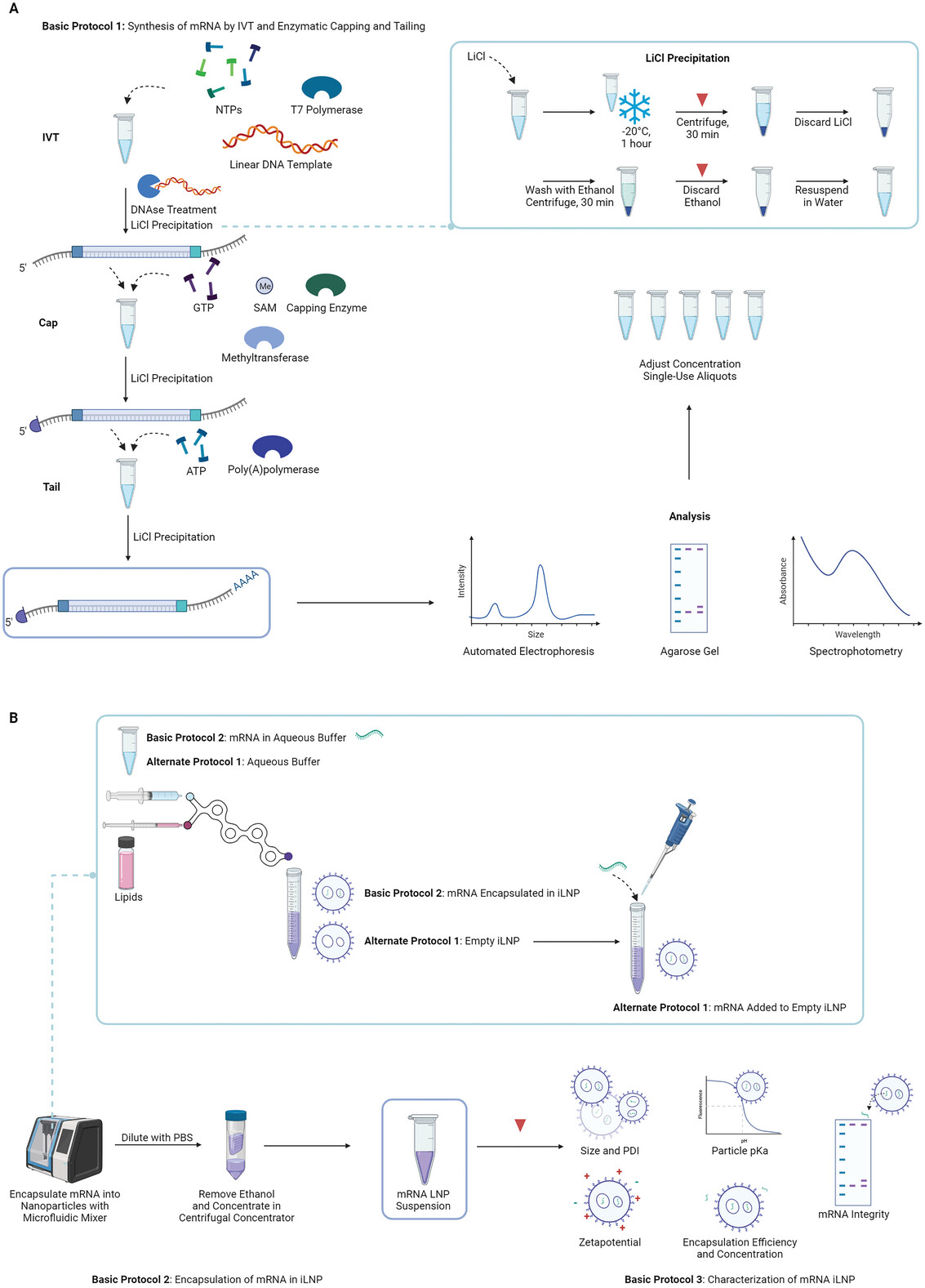
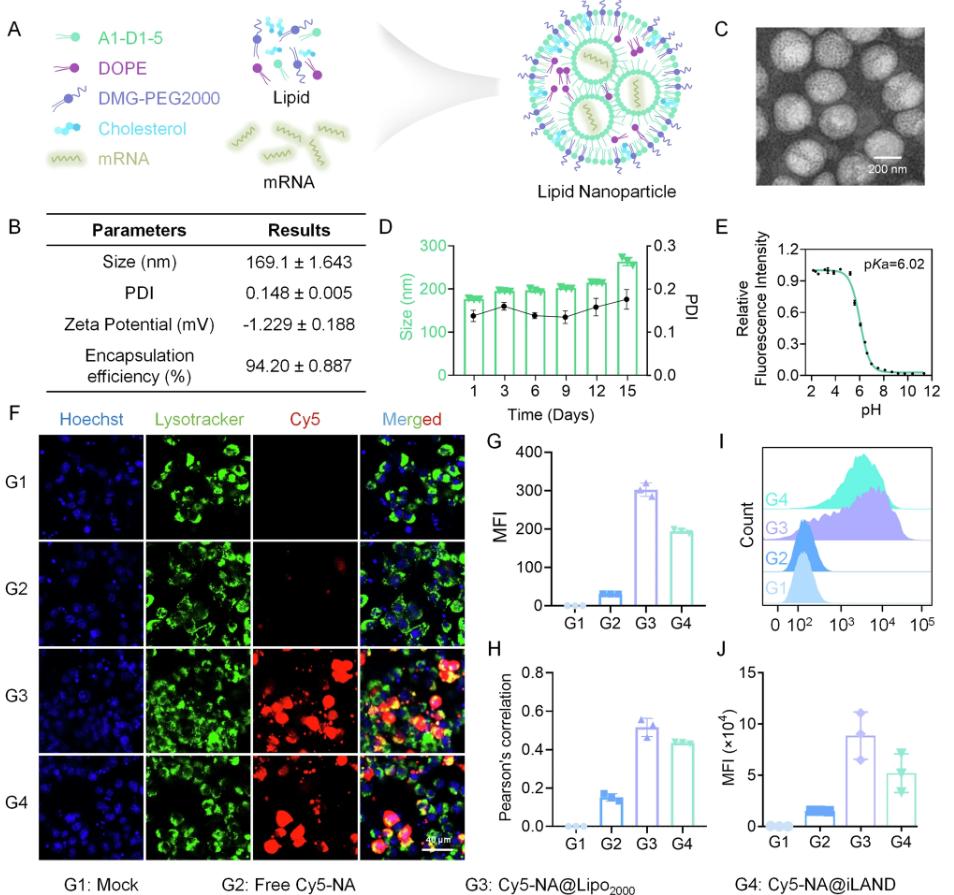
mRNA vaccines have attracted significant interest recently due to their success during the COVID-19 pandemic. Their success is attributed to advances in the design and encapsulation of mRNA into ionizable lipid nanoparticles (iLNPs). These vaccines are based on mRNA encapsulated in iLNPs, which are approximately 100 nm in diameter, and have a neutral surface charge and a dense electron-rich oily core. iLNP is currently the most clinically advanced mRNA delivery vehicle. In order to apply mRNA to these other areas, further optimization and development of iLNPs and mRNA may be required. Therefore, a method that can be used to make mRNA-iLNPs could allow more researchers to evaluate and advance them.
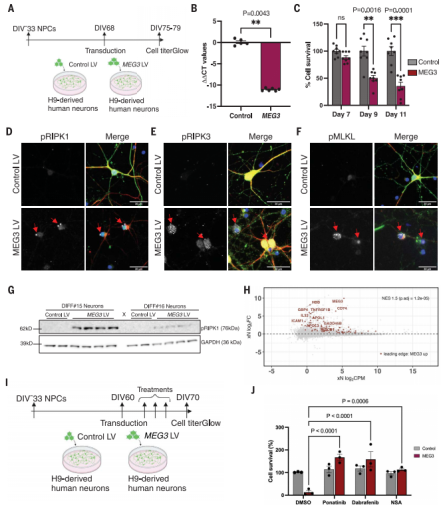
Neuronal cell loss is a defining feature of Alzheimer's disease (AD), but it is currently unclear how neurons die and how this relates to other defining features of the disease. Existing in vivo AD models only partially recapitulate the neuropathology of AD, with very minimal or no neuronal cell loss.
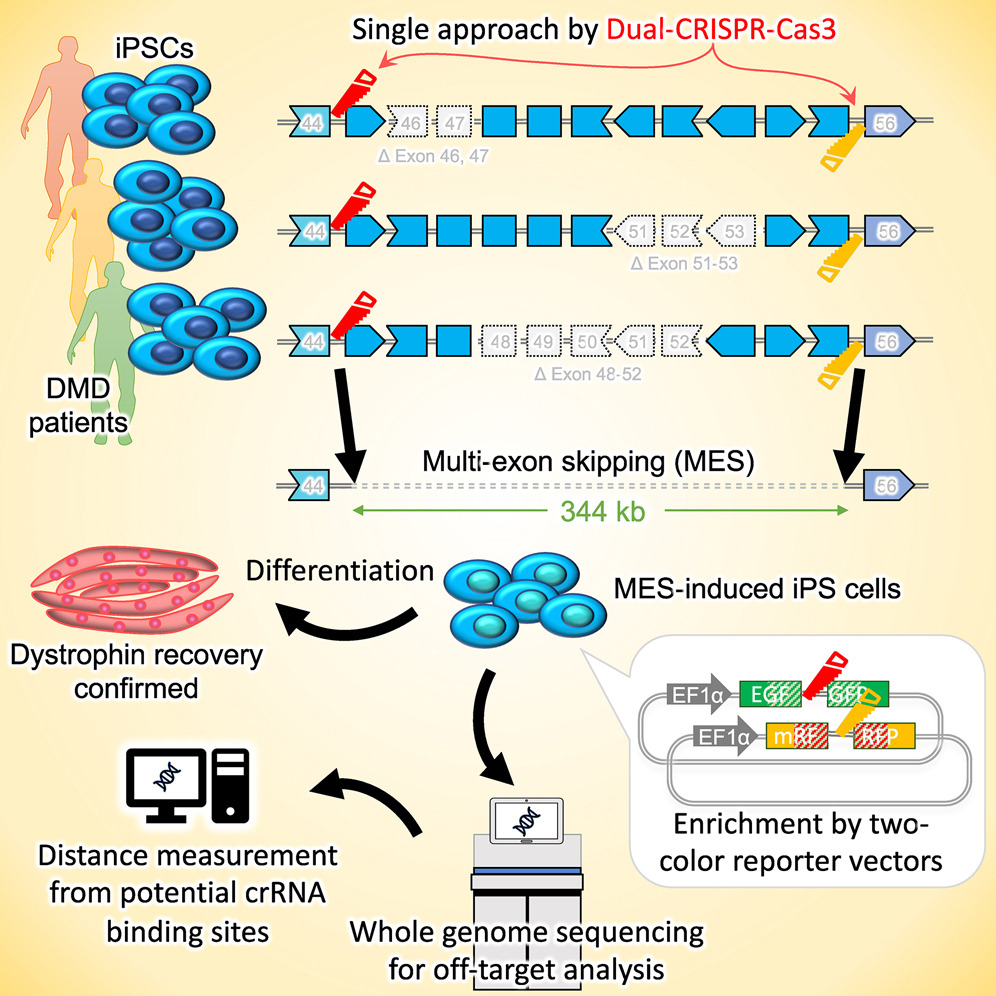
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe muscle degenerative disease caused by genomic mutations that cause a frameshift in the dystrophin gene. Exon skipping is a promising approach to restore dystrophin, and the CRISPR-Cas9 system is emerging as an emerging approach. However, techniques for inducing large deletions to cover target exons spread over hundreds of bases are limited.
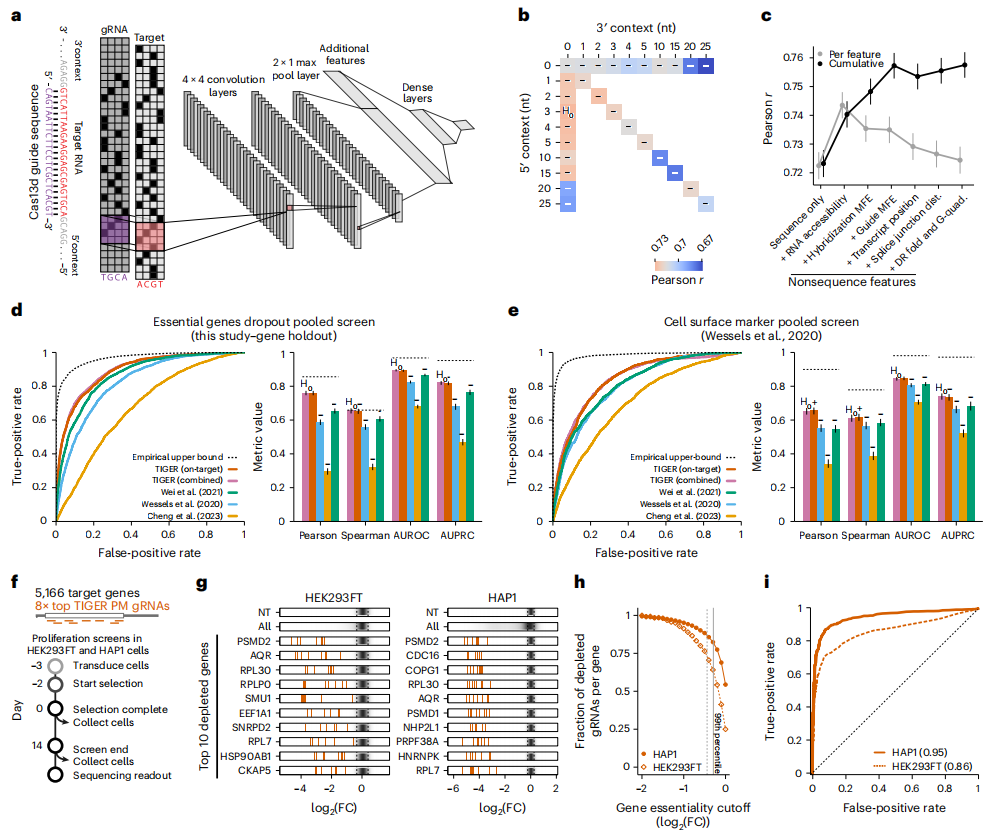
CRISPR gene editing technology has many applications in biomedicine and other fields, from the treatment of genetic diseases and cancer, to agricultural breeding, nucleic acid detection and so on. CRISPR gene editing relies on its two components, the guide RNA (gRNA) is responsible for identifying and targeting the target site, and the Cas enzyme is responsible for cutting the target site. CRISPR-Cas9 is the most widely used CRISPR system, but more and more studies have shown that it has potential risks for direct DNA cutting.